Myomectomy is a surgical procedure to remove uterine fibroids — also called leiomyomas. These common noncancerous growths appear in the uterus, usually during childbearing years, but they can occur at any age.
The doctor`s goal during myomectomy is to take out symptom-causing fibroids and reconstruct the uterus. Unlike a hysterectomy, which removes the entire uterus, a myomectomy removes only the fibroids and leaves the uterus intact.
Women who undergo myomectomy report improvement in fibroid symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure.
Myomectomy is recommended for fibroids causing symptoms that are troublesome or interfere with ones normal activities. The reasons to choose a myomectomy instead of a hysterectomy for uterine fibroids include:
- You plan to bear children
- Your doctor suspects uterine fibroids might be interfering with your fertility
- You want to keep your uterus
What are the treatment options and which one is best for me?
While up to 75 percent of reproductive aged women in certain populations may have uterine fibroids during their lifetime, the percentage of women who experience symptoms are fewer, about 25 percent. Treatments for symptomatic fibroids range from medications like pain relievers and hormones, such as oral contraceptives, to minimally invasive procedures like uterine artery embolization, HIFU to surgeries such as myomectomy or hysterectomy.
What you can expect
Depending on the size, number and location of fibroids, surgeon may choose one of the following surgical approaches to myomectomy.
Abdominal myomectomy
In abdominal myomectomy, gynecologist makes an open abdominal incision to access the uterus and remove fibroids. The doctor enters the pelvic cavity through one of two incisions:
- A horizontal bikini-line incision that runs about an inch (about 2.5 centimeters) above the pubic bone. This incision follows the natural skin lines, so it usually results in a thinner scar and causes less pain than a vertical incision does. It may be only 3 to 4 inches (8 to 10 centimeters), but may be much longer.
Because it limits the surgeon`s access to the pelvic cavity, a bikini-line incision may not be appropriate if one has large fibroids.
- A vertical incision that starts in the middle of the abdomen and extends from just below your navel to just above the pubic bone. This gives the surgeon greater access to uterus than a horizontal incision does and it reduces bleeding. It's rarely used, unless the uterus is so big that it extends up past one`s navel.
Minimal Invasive Surgery
Laparoscopic or Robotic myomectomy
In laparoscopic or robotic myomectomy the doctor accesses and removes fibroids through several small abdominal incisions.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy. The surgeon makes a cm sized incision in or near the bellybutton. Then he or she inserts a laparoscope ― a narrow tube fitted with a camera ― into the abdomen. The surgeon performs the surgery with instruments inserted through other small (5mm) incisions in the abdominal wall.
- Robotic myomectomy. Instruments are inserted through small incisions similar to those in a laparoscopic myomectomy, and the surgeon controls movement of instruments from a separate console.
Sometimes, the fibroid is cut into pieces and removed through a small incision in the abdominal wall. Other times the fibroid is removed through a mini- laparotomy incision in the abdomen so it can be removed without being cut into multiple small pieces. Rarely, the fibroid may be removed through an incision in the vagina (colpotomy).
Laparoscopic and robotic surgery use smaller incisions than abdominal or open myomectomy does. This means that one may have less pain, lose less blood and return to normal activities more quickly than with a laparotomy.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy
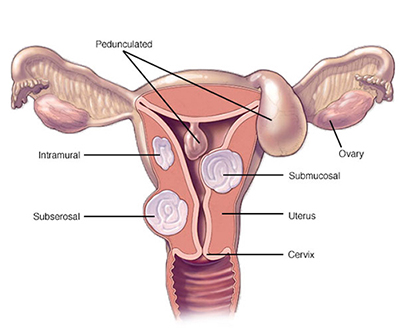
To treat fibroids that bulge significantly into your uterine cavity (submucosal fibroids), doctors may suggest a hysteroscopic myomectomy. The surgeon accesses and removes fibroids using instruments inserted through vagina and cervix into the uterus.
Rarely, your surgeon may use a laparoscope inserted through a small incision in your abdomen to view the pelvic organs and monitor the outside of the uterus during a complicated hysteroscopic myomectomy.
After the procedure
One can expect some vaginal spotting or staining for a few days up to six weeks, depending on the type of procedure one has had. One should defer prom pregnancy till about 3 months from surgery to allow for complete healing of uterus.
Why would I choose a minimally invasive procedure instead of a traditional surgery?
In many cases, minimally invasive procedures offer some significant advantages. Those advantages include fewer traumas during surgery and fewer complications after. With minimally invasive procedures, you typically enjoy a shorter hospital stay (or none at all), a faster recovery and less scarring.



